Introduction
The fusion of Information Technology (IT) with archaeology and heritage conservation is revolutionizing how we discover, document, and protect our past. Traditionally, archaeological research relied on manual excavation, physical documentation, and on-site preservation. However, with advancements in digital mapping, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and virtual reality, researchers can now explore historical sites with unprecedented accuracy while ensuring long-term conservation.
IT solutions are enabling archaeologists to analyse vast datasets, uncover hidden structures using remote sensing, and even restore damaged artifacts using AI-driven reconstruction. As a result, the integration of technology is enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility in heritage conservation, bridging the gap between history and the digital age.
1. Digital Mapping and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Satellite imagery and aerial photography aid in identifying potential excavation sites.
GIS databases help track excavation findings and site progress over time.
3D topographic mapping provides a detailed look at historical landscapes.

2. 3D Modelling and Digital Reconstruction
Many historical sites and artifacts are deteriorating due to natural disasters, pollution, or human activities. 3D scanning and modelling help in documenting these treasures.
3D laser scanning captures intricate details of ancient monuments.
Photogrammetry converts 2D images into realistic 3D models.
Digital twins of heritage sites allow for restoration planning and virtual tourism.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Archaeology
AI-powered tools are helping archaeologists analyse vast amounts of data more efficiently.
Pattern recognition algorithms identify inscriptions, pottery shards, and ancient texts.
AI-assisted translation deciphers ancient scripts faster than traditional methods.
Predictive modelling helps locate undiscovered archaeological sites based on historical data.
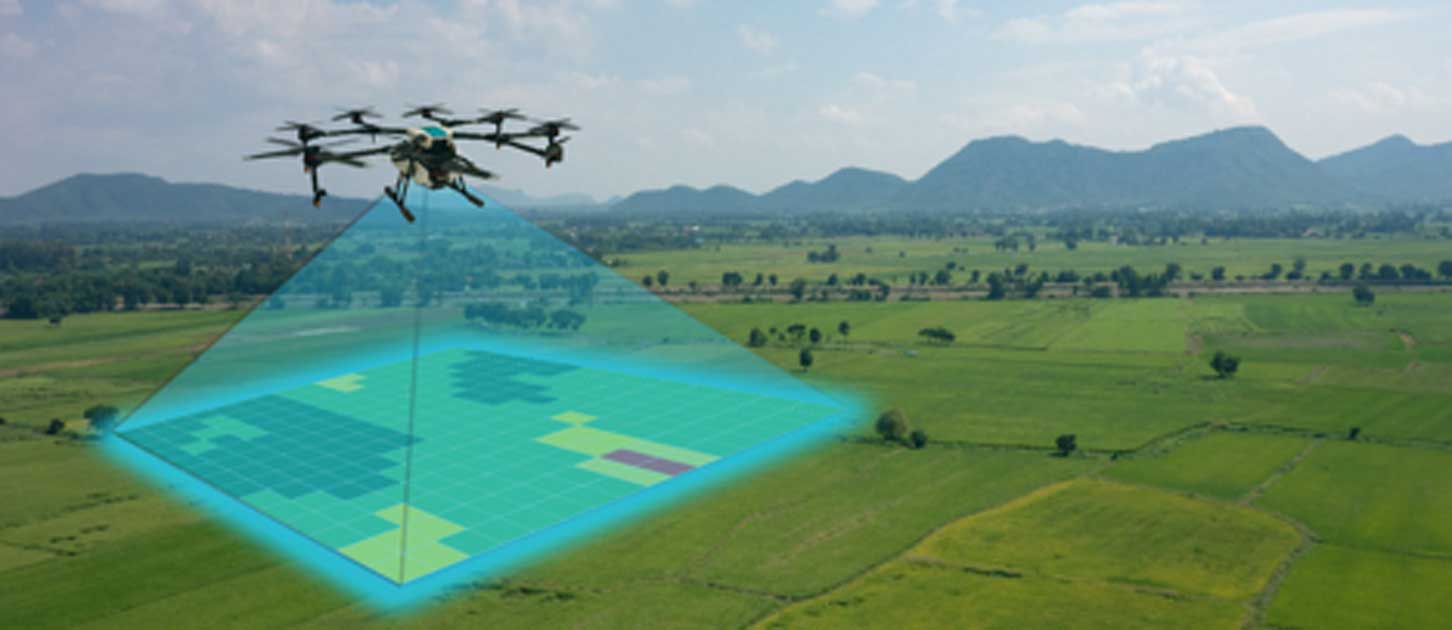
4. Drones and Remote Sensing Technologies
Archaeologists now use drones and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) to survey sites without disturbing them.
Drones capture high-resolution images of excavation sites from above.
LiDAR can penetrate dense forests to reveal buried structures.
Infrared and multispectral imaging detect subtle changes in soil and vegetation that hint at hidden ruins.
5. Blockchain for Artifact Authentication and Provenance Tracking
The illegal trade of historical artifacts is a growing issue. Blockchain technology ensures authenticity and prevents fraudulent transactions.
Decentralized ledgers provide immutable records of artifact ownership.
Smart contracts automate legal agreements between museums, collectors, and governments.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are being explored to digitally certify cultural artifacts.

6. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) for Heritage Education
Interactive technology is bringing history to life through AR and VR applications.
Virtual museums and site tours allow users to explore ancient civilizations from anywhere.
AR overlays on real-world sites provide historical context during visits.
Educational simulations let students experience historical events in a fully immersive environment.
7. Cloud Computing and Digital Archives
Digitization of historical records ensures long-term preservation and global accessibility.
Cloud-based databases store excavation reports, ancient manuscripts, and research papers.
AI-powered search engines help historians locate specific documents faster.
Digital backups protect against physical document deterioration.

8. Cybersecurity in Cultural Heritage Protection
As museums and archaeological organizations move online, cybersecurity has become essential.
Cybersecurity measures protect digital archives from hacking and data theft.
Blockchain and encryption safeguard sensitive research data.
AI-powered threat detection helps prevent cyberattacks on cultural institutions.
9. IoT (Internet of Things) for Site Monitoring
IoT sensors help archaeologists and conservationists monitor heritage sites in real time.
Environmental sensors detect changes in temperature, humidity, and pollution levels.
Structural sensors track the stability of ancient monuments.
Automated alerts notify conservationists of potential risks to fragile artifacts.

10. Robotics and Automation in Excavation
Traditional excavation is labour-intensive, but robotics and automation are changing the game.
Robotic arms assist in delicate artifact extraction.
Automated excavation tools speed up the digging process while maintaining precision.
Underwater robots explore submerged archaeological sites without human divers.
Conclusion: The Future of IT in Archaeology and Heritage Conservation
As technology continues to evolve, its impact on archaeology and heritage conservation will only grow stronger. AI, drones, IoT, and big data analytics are transforming how we uncover and interpret historical sites, while VR, AR, and blockchain are making heritage more accessible and secure. These innovations not only help us understand the past but also ensure that cultural legacies are preserved for future generations. By embracing IT solutions, archaeologists and conservationists are paving the way for a more connected and insightful exploration of human history—where the past meets the future in the digital realm.
