Introduction
The replication of human intelligence functions by machines, particularly computer systems, is known as artificial intelligence. Expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, and machine vision are some examples of specific AI applications.
How AI works?
Large volumes of labelled training data are ingested by AI systems, which then examine the data for correlations and patterns before employing these patterns to forecast future states. By studying millions of instances, an image recognition tool can learn to recognise and describe objects in photographs, just as a chatbot that is given examples of text can learn to produce lifelike dialogues with people. Generative AI approaches are able to produce realistic text, graphics, music, and other media.
The cognitive qualities that are prioritised in AI programming include the following:
Learning
This area of AI programming is concerned with gathering data and formulating the rules necessary to transform it into useful knowledge. The guidelines, also known as algorithms, give computing equipment detailed instructions on how to carry out a certain activity.
Reasoning
This area of AI programming is concerned with selecting the best algorithm to achieve a particular result.
Self-correction
This feature of AI programming is to continuously improve algorithms and make sure they deliver the most precise results.
Creativity
This branch of AI creates new images, texts, songs, and ideas using neural networks, rules-based systems, statistical techniques, and other AI tools.
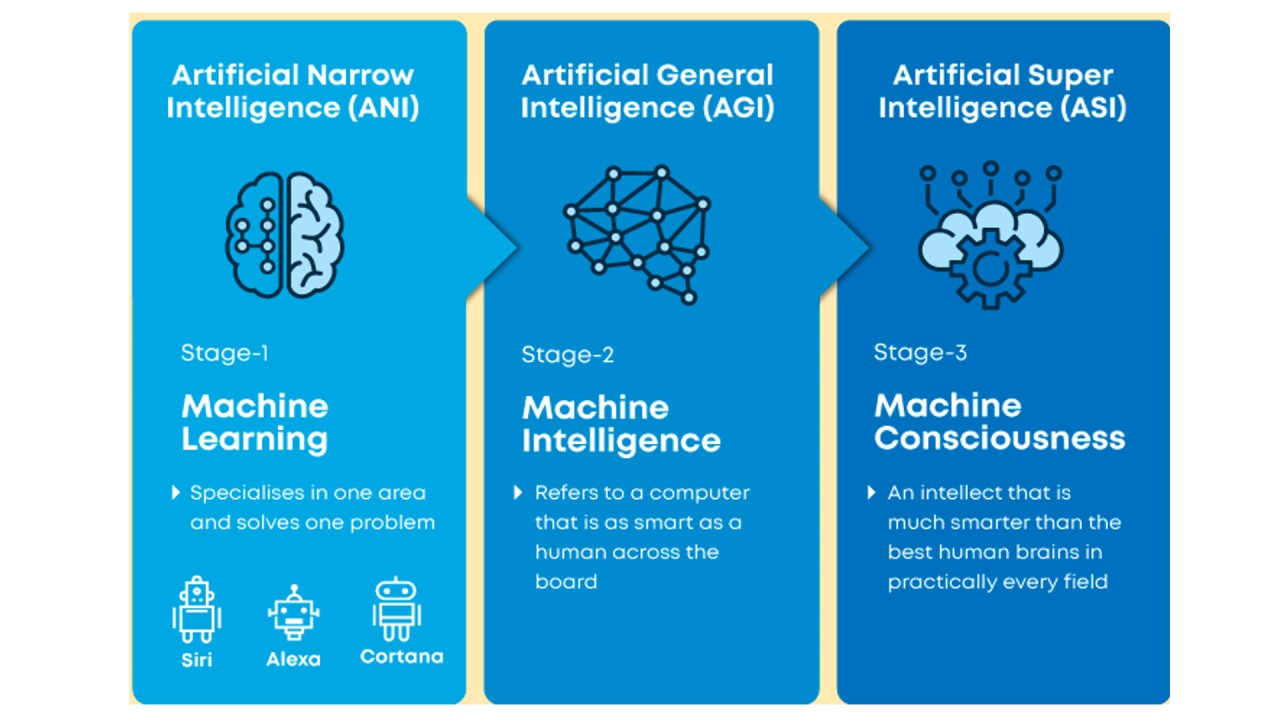
Stages of AI
Artificial Intelligence has three stages.
• Artificial Narrow Intelligence
• Artificial General Intelligence
• Artificial Super Intelligence
Artificial Narrow Intelligence
ANI, often referred to as Weak AI, is the stage of artificial intelligence that involves robots that can only carry out a limited range of certain activities. At this point, the machine only executes a list of predefined tasks; it is incapable of thinking. Siri, Alexa, self-driving cars, Alpha-Go, Sophia the humanoid, and other examples of weak AI can be found. The vast majority of AI-based systems created so far fall within the category of weak AI.
Artificial General Intelligence
AGI, also referred to as strong AI, is the stage in the development of artificial intelligence at which robots will have the capacity to think and act similarly to how we do as humans.
Strong AI has not yet been shown, but it is anticipated that we will soon be able to build machines that are just as intelligent as people.
Artificial Super Intelligence
The level of artificial intelligence at which computers will be more intelligent than people is known as artificial super intelligence. Currently, ASI is an imagined scenario when machines have overtaken the planet, as seen in science fiction films and books.
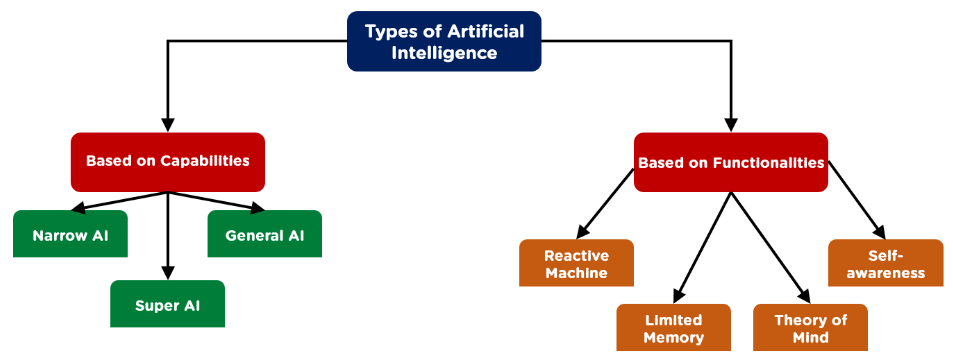
Types of AI
Four forms of AI can be distinguished, starting with task-specific intelligent systems that are widely used today and moving on to sentient systems, which do not yet exist.
Reactive machines
These AI systems are task-specific and lack memory. Deep Blue, the IBM chess programme that defeated Garry Kasparov in the 1990s, serves as an illustration. Deep Blue can recognise the pieces on a chessboard and make predictions, but because it lacks memory, it is unable to draw on its past learning to make predictions about the future.
Limited memory
These AI systems have a limited amount of memory, allowing them to draw on the past to guide present actions. This is how some of the decision-making processes of self-driving automobiles are constructed.
Theory of mind
Theory of mind is a term used in psychology. When applied to AI, it suggests that the technology would be socially intelligent enough to comprehend emotions. This kind of AI will be able to forecast behaviour and deduce human intentions, which is a capability required for AI systems to become essential members of human teams.
Self-awareness
In this category, AI programmes are conscious because they have a sense of who they are. Self-aware machines are aware of their own conditions. There is currently no such AI.
Advantages of AI
These are some of the benefits of AI.
Good at detail-oriented jobs
AI has shown to be just as good as or better than doctors at diagnosing some illnesses, such as breast cancer and melanoma.
Reduced time for data-intensive tasks
AI is frequently used to speed up big data analysis in data-intensive businesses including banking and securities, pharmaceuticals, and insurance. For instance, financial services frequently utilise AI to analyse loan applications and identify fraud.
Saves labor and increases productivity
The usage of warehouse automation, which increased during the pandemic and is anticipated to rise with the incorporation of AI and machine learning, is one example of how this saves labour and boosts productivity.
Delivers reliable results
Even small enterprises may contact customers in their local tongue thanks to the greatest AI translation systems, which offer high levels of consistency.
Can improve customer satisfaction through personalization
Personalization can increase customer satisfaction since AI is able to tailor websites, messages, adverts, and content to specific users.
Virtual agents using AI are constantly accessible
AI programmes work around-the-clock because they don't need to sleep or take breaks.

Conclusion
AI has taken up a significant amount of human life. Humans' requirements for food, medicine, and shelter are all met by a variety of industries. Data is the main source for analysing needs and the ensuing management of resources.
Without a question, AI systems have demonstrated their ability to complete these jobs by selecting the optimum course of action from a pool of relevant facts. The advancements in hardware, software, and technology have made it possible for AI to handle many complicated tasks more effectively.
