Introduction
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of Industry 4.0, promising to revolutionize industrial operations with unprecedented connectivity, speed, and efficiency. Industry 4.0, characterized by the integration of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, aims to create smart factories where machines and systems communicate and collaborate seamlessly. 5G, with its ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and massive device connectivity, is set to be the catalyst that drives these transformations, enabling more sophisticated automation, real-time data processing, and enhanced operational agility. In this blog, we explore the profound impact of 5G on Industry 4.0, examining its advantages, benefits, use cases, and various types of applications that are shaping the future of manufacturing and industrial operations.
Advantages of 5G in Industry 4.0
Ultra-Low Latency 5G technology offers latency as low as one millisecond, which is crucial for real-time applications in Industry 4.0. This ultra-low latency enables near-instantaneous communication between machines, systems, and sensors, ensuring that critical operations can be performed without delay. For example, in automated manufacturing processes, the rapid exchange of data between robotic arms and control systems can significantly enhance precision and reduce errors.
High Bandwidth The high bandwidth provided by 5G allows for the transmission of large volumes of data at unprecedented speeds. This is essential for supporting the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices, sensors, and advanced manufacturing equipment. For instance, in a smart factory, machines equipped with sensors continuously generate data related to performance, maintenance needs, and environmental conditions. With 5G, this data can be transmitted and analyzed in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. This high bandwidth also supports augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications, which can be used for training, remote assistance, and virtual prototyping.
Massive Device Connectivity 5G can support up to one million devices per square kilometer, which is significantly higher than previous generations of mobile networks. This massive connectivity is crucial for Industry 4.0, where numerous IoT devices and sensors are deployed to monitor and control industrial processes. In a smart manufacturing plant, hundreds of sensors can be embedded in machinery, production lines, and even the facility itself to collect data on various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration. The ability to connect and manage these devices efficiently ensures that all parts of the production process are optimized and that resources are used effectively.
Enhanced Reliability 5G networks are designed to provide highly reliable communication, which is essential for mission-critical applications in industrial environments. Enhanced reliability ensures that data transmission is consistent and uninterrupted, reducing the risk of communication failures that could lead to production halts or safety issues. For example, in the oil and gas industry, real-time monitoring of drilling operations and pipeline integrity is crucial to prevent accidents and environmental hazards. With 5G, companies can ensure that their monitoring systems are always connected and operational, providing continuous oversight and early detection of potential problems.
Energy Efficiency 5G technology is designed to be more energy-efficient than its predecessors, which is an important consideration for sustainable Industry 4.0 initiatives. Lower energy consumption not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. For instance, in smart factories, energy-efficient 5G networks can help reduce the overall energy consumption of connected devices and systems, contributing to greener manufacturing processes.
Benefits of 5G in Industry 4.0
Increased Operational Efficiency The integration of 5G technology in Industry 4.0 significantly enhances operational efficiency. Real-time data analytics enabled by 5G allows for immediate decision-making and process optimization. For example, manufacturers can use 5G to monitor production lines in real time, quickly identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and adjusting on the fly. This leads to smoother operations, reduced waste, and higher productivity.
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability 5G's ability to support a high density of connected devices provides industries with the flexibility to scale their operations as needed. Companies can easily expand their network of connected machines and sensors without worrying about network congestion or performance degradation. For instance, a factory can start with a few automated machines and gradually increase the number of connected devices as production demands grow.
Improved Safety and Maintenance The real-time monitoring capabilities provided by 5G enhance safety and maintenance in industrial environments. Continuous data collection and analysis allow for predictive maintenance, identifying potential equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime and maintenance costs while ensuring the safety of workers. For example, in a chemical plant, sensors connected via 5G can detect changes in pressure or temperature that indicate potential leaks or equipment malfunctions.
Reduced Latency in Critical Applications The ultra-low latency of 5G is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time responsiveness. In industrial automation, latency can be the difference between a smoothly running process and a costly error. For instance, in robotic assembly lines, precise timing is crucial for ensuring that components are assembled correctly. 5G's low latency ensures that robots receive and execute commands instantly, minimizing the risk of errors and improving the overall quality of the finished products.
Support for Advanced Technologies 5G provides the necessary infrastructure to support advanced technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and edge computing. These technologies have numerous applications in Industry 4.0, from training and simulation to remote assistance and quality control. For example, AR can be used to provide workers with real-time, hands-free access to assembly instructions, enhancing productivity and reducing errors. VR can be used for immersive training programs, allowing employees to practice complex tasks in a virtual environment before performing them on the actual production floor.

Use Cases of 5G in Industry 4.0
Smart Manufacturing 5G enables the creation of smart factories where machines, sensors, and systems are interconnected and communicate in real time. This connectivity allows for seamless data exchange and process optimization, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. For example, a smart factory can use 5G to monitor production lines, automatically adjust machine settings to optimize output, and detect potential issues before they cause downtime. Companies like Bosch and Siemens are leveraging 5G to enhance their manufacturing processes, resulting in significant cost savings and improved product quality.
Autonomous Vehicles In industrial settings, autonomous vehicles such as forklifts, drones, and AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) rely on 5G for precise navigation and real-time communication. These vehicles can transport materials and products within a facility without human intervention, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. For instance, in a warehouse, AGVs can use 5G to navigate through aisles, avoid obstacles, and coordinate with other vehicles to optimize the flow of goods. This automation reduces the risk of accidents and allows for continuous operation, enhancing overall productivity.
Remote Monitoring and Control 5G enables remote monitoring and control of industrial processes, allowing operators to manage equipment and systems from a central location. This capability is particularly useful in industries such as oil and gas, where facilities may be located in remote or hazardous environments. For example, sensors connected via 5G can monitor the condition of pipelines, detecting leaks or pressure changes in real time. Operators can then take immediate action to address issues, reducing the risk of environmental damage and ensuring the safety of workers. This remote capability also allows for more efficient resource allocation, as maintenance teams can be dispatched only when needed.
Augmented Reality for Maintenance and Training Augmented reality (AR) applications, supported by 5G, provide real-time information and guidance to workers performing maintenance or training tasks. For example, a technician wearing AR glasses can receive step-by-step instructions overlaid on the equipment they are working on, reducing the risk of errors and speeding up the repair process. In training scenarios, AR can simulate complex tasks, allowing workers to practice and gain confidence before performing them in the real world. Companies like PTC and Microsoft are developing AR solutions that leverage 5G to provide real-time, interactive experiences for industrial applications.
Supply Chain Optimization 5G enhances supply chain management by providing real-time visibility and tracking of goods throughout the entire supply chain. Smart sensors and IoT devices connected via 5G can monitor the condition and location of products during transportation and storage, ensuring that they reach their destination in optimal condition. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, 5G-enabled sensors can track the temperature and humidity of vaccines during transit, ensuring they remain within the required conditions.

Types of 5G Applications in Industry 4.0
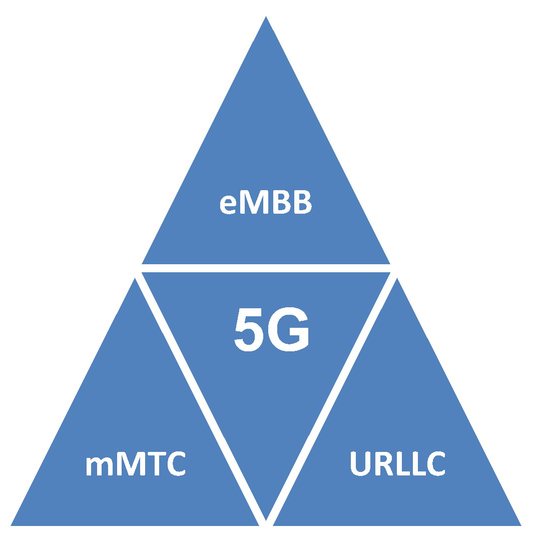
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) provides high-speed internet access and supports applications requiring large data transfers, such as high-definition video streaming and virtual reality. In Industry 4.0, eMBB enables remote monitoring and control, as well as the use of AR and VR for training and maintenance. For example, technicians can use VR headsets to perform virtual inspections of equipment, reducing the need for on-site visits and improving efficiency.
Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) supports the connection of many IoT devices and sensors, enabling extensive data collection and monitoring. In a smart factory, mMTC allows for the deployment of thousands of sensors to monitor various parameters such as temperature, humidity, and machine performance. This data can be analyzed in real time to optimize production processes and ensure the efficient operation of machinery.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) provide highly reliable and low-latency connectivity, essential for mission-critical applications. In industrial automation, URLLC ensures that machines and systems can communicate and respond in real time, enabling precise control and coordination. For example, in autonomous vehicle operations, URLLC ensures that vehicles can navigate and avoid obstacles with minimal delay, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Edge Computing Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and improves the efficiency of real-time applications. In Industry 4.0, edge computing enables real-time data analysis and decision-making at the production site. For example, in a manufacturing plant, edge computing can be used to analyze data from sensors on the production line, allowing for immediate adjustments to optimize output and reduce waste.
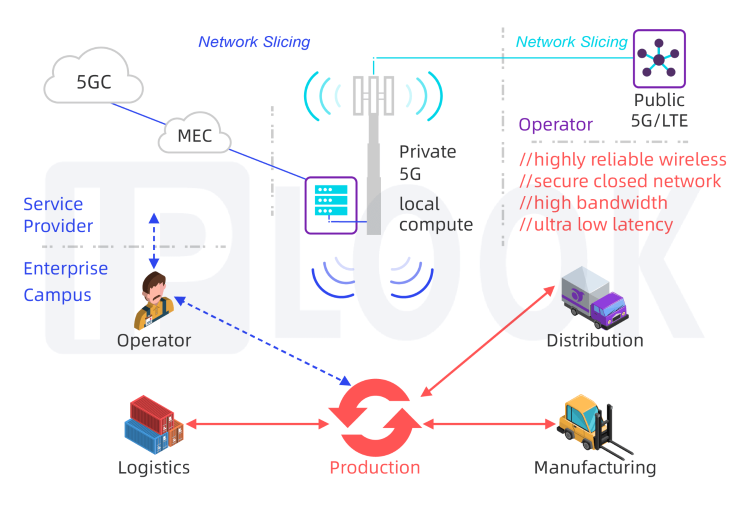
Network Slicing Network slicing allows for the creation of multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network, each tailored to specific applications or requirements. This enables industries to allocate network resources more efficiently and ensure that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency. For example, a smart factory can use network slicing to prioritize real-time control and monitoring applications, ensuring that they operate without interruption, while less critical applications such as data backup can be assigned to a lower-priority slice.
Conclusion
The integration of 5G technology into Industry 4.0 is set to revolutionize industrial operations, driving unprecedented levels of efficiency, reliability, and innovation. With its ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and massive connectivity, 5G enables real-time data processing, advanced automation, and enhanced operational agility. The advantages and benefits of 5G are evident across various applications, from smart manufacturing and autonomous vehicles to remote monitoring and augmented reality. As industries continue to embrace these technologies, the future of manufacturing and industrial operations looks promising, characterized by greater productivity, improved safety, and sustainable growth. The evolution of 5G and its impact on Industry 4.0 underscores the importance of continued investment and innovation in next-generation connectivity solutions.
