Introduction
The rise of digital transformation across industries has brought about significant advancements in information technology (IT), which in turn has greatly impacted the cybersecurity industry.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the role of IT technology has evolved from traditional protection methods to advanced systems that enable real-time detection, automated responses, and proactive defense mechanisms. With innovations like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and blockchain, IT has become integral to maintaining the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data in an increasingly connected world.
1. Automation and AI-Driven Security
AI and Machine Learning (ML): IT has enabled the use of AI and ML to predict and detect potential threats in real time. These systems learn from vast amounts of data and can automatically detect anomalies, allowing for faster responses to emerging threats.
Automation: Automation in cybersecurity allows repetitive tasks such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and threat detection to be handled by software, freeing up human resources for more complex tasks. This also reduces the chance of human error.
2. Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools utilize advanced IT techniques to monitor, detect, and respond to cyber threats across devices. These systems can identify suspicious activities on endpoints and contain threats before they escalate.
Behavioral Analytics: By leveraging big data analytics, cybersecurity solutions can monitor and analyze user behavior. Any deviations from normal activity patterns can trigger alerts, helping to identify insider threats or compromised credentials.
3. Cloud Security
Cloud-Based Security Solutions: As businesses migrate to cloud environments, IT technology ensures that security measures evolve. Cloud-based cybersecurity tools, such as firewalls, encryption, and access control systems, help protect data and applications in these environments.
Zero Trust Architecture: IT advancements have given rise to the “Zero Trust” model, where no entity—whether inside or outside the network—is trusted by default. This architecture, supported by identity and access management (IAM) systems, restricts access to data based on user roles and authentication protocols.
4. Data Encryption and Privacy
Encryption: Advances in IT have improved encryption methods, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure, whether in transit or at rest. This has become crucial with the increasing need for data protection across industries like finance, healthcare, and legal sectors.
Privacy and Compliance: IT technology has helped cybersecurity teams ensure compliance with global privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Automated compliance tools assist companies in adhering to these standards and avoiding hefty fines.
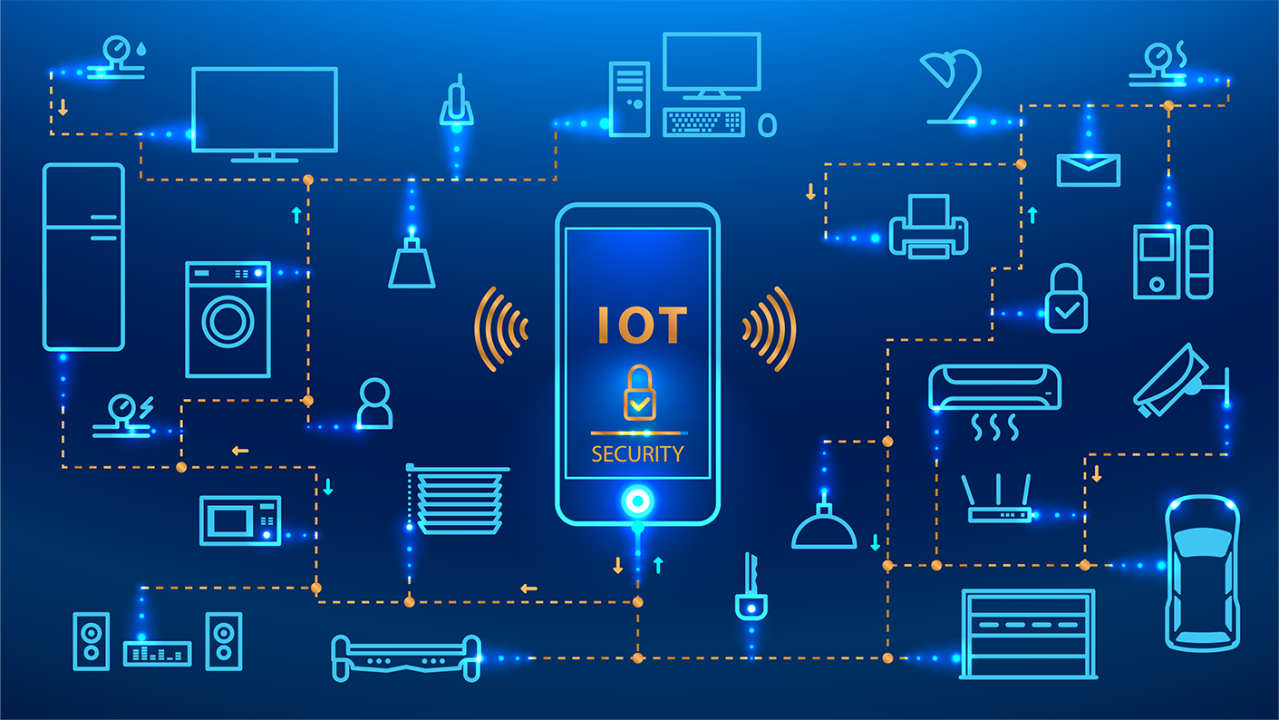
5. Cybersecurity in IoT
Internet of Things (IoT) Security: As IoT devices become more widespread, IT technology has stepped in to provide security solutions for this expanding attack surface. Solutions such as device authentication, secure communication protocols, and network segmentation help mitigate risks in IoT ecosystems.

6. Blockchain and Cybersecurity
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain, an IT innovation, offers potential for enhancing cybersecurity through decentralized and tamper-proof systems. Blockchain’s secure, transparent, and immutable ledger can provide solutions for securing transactions, identity management, and data storage.
7. Cybersecurity Threat Intelligence
Real-Time Threat Intelligence: IT infrastructure facilitates the collection and analysis of cyber threat intelligence from global sources. This intelligence is shared across networks, enabling proactive defense strategies by anticipating and preparing for potential attacks.
Collaboration Platforms: IT platforms enable better collaboration between cybersecurity experts, governments, and businesses to address emerging cyber threats collectively.
8. Cybersecurity as a Service (CSaaS)
Managed Security Services: IT technology has given rise to cybersecurity as a service (CSaaS), where companies can outsource their cybersecurity needs to specialized providers. This allows smaller organizations to access enterprise-level security without the need for in-house expertise.
9. Enhanced User Awareness and Training
Security Training Tools: IT technology powers various training platforms that can educate employees on the best cybersecurity practices through simulations and interactive courses. Gamified learning experiences and phishing simulations increase awareness and help reduce human errors leading to breaches.
10. Integration with IT Systems and DevSecOps
DevSecOps: IT technology integrates security into the software development lifecycle with the DevSecOps model. This ensures that security is built into applications from the outset, rather than as an afterthought. Automated security testing tools scan code for vulnerabilities during development.

Conclusion
In conclusion, IT technology has fundamentally reshaped the cybersecurity landscape, enabling organizations to better defend against evolving threats. From advanced AI-driven detection systems to cloud-based security solutions and IoT protection, the integration of IT has made cybersecurity more efficient, scalable, and resilient. As technology continues to advance, the cybersecurity industry will rely on these innovations to stay ahead of emerging risks and maintain the security and privacy of digital assets.
